Reading Notes of TZX
Table of Contents
- 1. ☰
- 1.1. Meta Notes
- 1.2. Books
- 1.2.1. DONE Combo #1
- 1.2.2. INPROGRESS Combo #2
- 1.2.3. DONE JavaScript: The Good Parts
- 1.2.4. DONE Domain Specific Languages
- 1.2.5. INPROGRESS Effective Java
- 1.2.6. DONE Don't Make Me Think
- 1.2.7. DONE Clean Code
- 1.2.8. INPROGRESS Deep Learning
- 1.2.9. INPROGRESS Async JavaScript
- 1.2.10. INPROGRESS ng-book2
- 1.2.11. INPROGRESS Combo #3: SLAM
- 2. Writing Rules
- 3. TODO Methodology
- 4. Code Reading
- 4.1. DONE
- 4.2. DONE
- 4.3. INPROGRESS
- 4.4. TODO
- 4.5. DONE
- 4.6. DONE
- 4.7. INPROGRESS
- 4.8. TODO Awesome Micro NPM Packages
- 4.9. TODO facebookresearch/Detectron: FAIR's research platform for object detection research, implementing popular algorithms like Mask R-CNN and RetinaNet.
- 4.10. SQL
- 4.10.1. sql 101
- 4.10.2. sql select, distinct, where, and/or/not, order by, insert into, null, update, delete
- 4.10.3. sql limits, min/max, count/avg/sum, like, between, alias
- 4.10.4. sql join (inner, outer (left,right,full))
- 4.10.5. sql union, group by, having, exsists, any/all
- 4.10.6. sql select into, insert into, null
- 4.10.7. sql constraints
1 ☰
1.1 Meta Notes
1.2 Books
1.2.1 DONE Combo #1
1.2.3 DONE JavaScript: The Good Parts
1.2.4 DONE Domain Specific Languages
1.2.5 INPROGRESS Effective Java
1.2.6 DONE Don't Make Me Think
1.2.7 DONE Clean Code
1.2.8 INPROGRESS Deep Learning
1.2.9 INPROGRESS Async JavaScript
1.2.10 INPROGRESS ng-book2
1.2.11 INPROGRESS Combo #3: SLAM
2 Writing Rules
- 参考 Chinese copywriting guidelines for better written communication/中文文案排版指北
- 其他
- 标点: 使用英文标点
- 缩进:
- markdown 使用四个空格, 使用
-来做 bullet - org-mode 使用两个空格 (虽然我喜欢四个), 使用
-和+交替来做 bullet
- markdown 使用四个空格, 使用
- 空行:
- markdown 多加空行, e.g. 在块元素前后加空行 (但不能有连续空行)
- org-mode 少加空行, e.g. 在块元素前后不加空行 (能少则少, 不同 chap/sec/subsec 之间也不加空行)
Why? 因为 org-mode 的折叠可能会把空行折叠进去, 也可能不. 这样很 不 consistent. 所以直接去掉.
3 TODO Methodology
有困难解决困难。没有困难创造困难,然后解决困难。
3.1 Project-based Learning
学习一定应该是“项目型的学习”(Project-based Learning)以及带着解决问 题的目标去学习,而这目标必须是某个现实的目标,而不是一种教科书上的编造。
Students learn about a subject by working for an extended period of time to investigate and respond to a complex question, challenge, or problem. It is a style of active learning and inquiry-based learning. PBL contrasts with paper-based, rote memorization, or teacher-led instruction that presents established facts or portrays a smooth path to knowledge by instead posing questions, problems or scenarios.
3.2 Structured Thinking
3.3 Deliberate Practice
4 Code Reading
4.1 DONE https://github.com/4ker/JavaAOP
AOP 的一个实现, 大致逻辑是:
- 用 Java 的反射功能可以拿到一个对象的 method 和 field (还可以包括继承来的)
- 然后用 Java 的 Proxy 给原来的对象封装一层, 在函数调用的时候插入逻辑
- 插入的逻辑标记在 annotation 里面
4.2 DONE https://github.com/4ker/gradle-build-scan-quickstart
很多有用的文档: _ Learn groovy in y minutes ::
- https://github.com/adambard/learnxinyminutes-docs/blob/master/groovy.html.markdown
- IntelliJ: Tools – Groovy Console
- [l, i, s, t], [m: a, p: map]
- {function block}
内容主要有: (setq-default tab-width 2)
- gradle 相关命令
- groovy 语法
gradle tasks gradle help --task checkStyleMain gradle properties
4.3 INPROGRESS https://github.com/4ker/Photo-Sphere-Viewer
4.3.1 Intro & Compare with Pannellum
Photo Sphere Viewer is a JavaScript library that allows you to display 360×180 degrees panoramas on any web page. Panoramas must use the equirectangular projection and can be taken with the Google Camera, the Ricoh Theta or any 360° camera.
I forked the original Photo Sphere Viewer by Jérémy Heleine to provide a better JS architecture and a bunch of new features.
很明确, 是 folk 了别人的代码, 提供了更好的模块化. 所以这个代码值得看.
之前看了另一份代码: https://github.com/mpetroff/pannellum/, 这份代码 star 数量更多, 但是几乎没啥模块化, 而且去掉了 three.js 的依赖 (我觉得要想不仅仅是全景浏览, three.js 是必要的). pannellum (破耐乐目), 接口很有意思, 可以参考, 尤其是用了 Google 街景全景图的指定方式: https://developers.google.com/streetview/spherical-metadata.
再有 pannellum 里面给了一个 python 脚本来生成 multires panoramas, 全 equirectangular 投影不同的是, 这个用了 box projection, 而且每个方形都用了金字塔. 这个投影很规整. 数据看上去也比较清晰, 而且用 CSS 3D 就能渲染, 挺牛逼.
pannellum 的图片也不错, 都是 svg sprites, 然后用 css 引进来用. 页面做的赏心悦目. 简洁 页面做的赏心悦目. 简洁. 移动端重力感应和触屏拖拽也处理的很好. 它把自己定位为一个嵌 iframe 的加载器. 可惜.
multires panoramas 文档:
- https://krpano.com/docu/multires/
- https://krpano.com/html5multires/ 老师之前给看过这个 45 GB 的全景图, 太清晰
4.3.2 Usage
<link rel="stylesheet" href="Photo-Sphere-Viewer/dist/photo-sphere-viewer.min.css">
<script src="three.js/three.min.js"></script>
<script src="D.js/lib/D.min.js"></script>
<script src="uevent/uevent.min.js"></script>
<script src="doT/doT.min.js"></script>
<script src="Photo-Sphere-Viewer/dist/photo-sphere-viewer.min.js"></script>
<script>
var viewer = PhotoSphereViewer({
container: 'container-id',
panorama: 'path/to/panorama.jpg'
});
</script>
其中
- doT 是一个模板引擎, 其实现在用 es6 的 `template` 就行. pass.
- uEvent 是作者 folk 并修改了了 jeromeetienne 的 event emitter microlibrary - 20lines -for node and browser; 后者是 three.js 网红, 原来写过 tQuery 啥的 (个人感觉没啥使用的意义), 还有 VR.js.
- D.js 是 tiny promise/A+ implementation
史上最易读懂的 Promise/A+ 完全实现 Promise/A+ 是 promise 的一个 spec. 在 spec 里, Promise 只有一个 then 方法 (两个参数, 一个 resolve, 一个 reject, then 返回一个新的 promise), 没有 catch,race,all 等方法, 甚至没有构造函数 promise 的三种状态. 不同 Promise 的实现需要可以相互调用 (interoperable). Promise 的三种状态: pending, fulfilled, rejected.
4.4 TODO https://github.com/4ker/gtor
4.5 DONE https://github.com/4ker/q
这个文档很赞. 可以多读几遍.
4.5.1 啥是 promise
A promise is an object that represents the return value or the thrown exception that the function may eventually provide. A promise can also be used as a proxy for a remote object to overcome latency. 就是一个许诺返回的对象. 当然, 值返回不成功, 就返回一个异常.
Q.fcall(promisedStep1)
.then(promisedStep2)
.then(promisedStep3)
.then(promisedStep4)
.then(function (value4) {
// Do something with value4
})
.catch(function (error) {
// Handle any error from all above steps
})
.done();
常规使用方法是, 一个 promise 可以 .then 来处理.
then 方法的输入是两个函数, 一个 resolver, 一个 rejector.
promiseMeSomething()
.then(function (value) {
...
}, function (reason) {
...
});
而且 then 返回的也是一个 promise, 这样就能不断 propagate 出去. bubble out.
fail 是一种 then(null, resolver) 的语法糖.
4.5.2 chaining
// nested chaining
return getUsername()
.then(function (username) {
return getUser(username)
.then(function (user) {
// if we get here without an error,
// the value returned here
// or the exception thrown here
// resolves the promise returned
// by the first line
})
});
// handler
return getUsername()
.then(function (username) {
return getUser(username);
})
.then(function (user) {
// if we get here without an error,
// the value returned here
// or the exception thrown here
// resolves the promise returned
// by the first line
});
// 按情况混用
function authenticate() {
return getUsername()
.then(function (username) {
return getUser(username);
})
// chained because we will not need the user name in the next event
.then(function (user) {
return getPassword()
// nested because we need both user and password next
.then(function (password) {
if (user.passwordHash !== hash(password)) {
throw new Error("Can't authenticate");
}
});
});
}
4.5.3 combination
return Q.all([
eventualAdd(2, 2),
eventualAdd(10, 20)
]);
4.5.4 sequential
// 对 initialVal 进行一系列操作, 怎么写?
return foo(initialVal).then(bar).then(baz).then(qux);
// 输入是 initialVal 和 funcs
var funcs = [foo, bar, baz, qux];
// 一般实现
var result = Q(initialVal);
funcs.forEach(function (f) {
result = result.then(f);
});
return result;
// 用 reduce
return funcs.reduce(function (soFar, f) {
return soFar.then(f);
}, Q(initialVal));
// 用 compact 的实现
return funcs.reduce(Q.when, Q(initialVal));
// TODO: check Q.when 是否就是 Q.when = p => p.then
The when function is the static equivalent for then.
return Q.when(valueOrPromise, function (value) {
}, function (error) {
});
4.5.5 then end
// return it
return foo()
.then(function () {
return "bar";
});
// end it
return foo()
.then(function () {
return "bar";
});
// either return it
return foo()
.then(function () {
return "bar";
});
// or end it
foo()
.then(function () {
return "bar";
})
.done();
4.5.6 create a promise
// from a func that returns
return Q.fcall(function () {
return 10;
});
// from a func that throws
return Q.fcall(function () {
throw new Error("Can't do it");
});
// from a fcall
return Q.fcall(eventualAdd, 2, 2);
4.5.7 deferred
callback to promise:
// wrap it
var deferred = Q.defer();
FS.readFile("foo.txt", "utf-8", function (error, text) {
if (error) {
deferred.reject(new Error(error));
} else {
deferred.resolve(text);
}
});
return deferred.promise;
// use it
deferred.reject(new Error("Can't do it"));
4.5.8 the promise
function requestOkText(url) {
return Q.Promise(function(resolve, reject, notify) {
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open("GET", url, true);
request.onload = onload;
request.onerror = onerror;
request.onprogress = onprogress;
request.send();
function onload() {
if (request.status === 200) {
resolve(request.responseText);
} else {
reject(new Error("Status code was " + request.status));
}
}
function onerror() {
reject(new Error("Can't XHR " + JSON.stringify(url)));
}
function onprogress(event) {
notify(event.loaded / event.total);
}
});
}
4.6 DONE https://github.com/district10/You-Dont-Need-jQuery
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$('selector');
// Native
document.querySelectorAll('selector');
document.getElementsByClassName('class');
document.getElementById('id');
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$el.css({ color: '#f01' });
// Native
el.style.color = '#f01';
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$el.addClass(className);
$el.removeClass(className);
$el.toggleClass(className);
// Native
el.classList.add(className);
el.classList.remove(className);
el.classList.toggle(className); // 这些东西不是 list 操作.
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$el.remove();
// Native
el.parentNode.removeChild(el);
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$el.append('<div id="container">Hello World</div>');
// Native (HTML string)
el.insertAdjacentHTML('beforeend', '<div id="container">Hello World</div>');
// Native (Element)
el.appendChild(newEl);
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$el.prepend('<div id="container">Hello World</div>');
// Native (HTML string)
el.insertAdjacentHTML('afterbegin', '<div id="container">Hello World</div>');
// Native (Element)
el.insertBefore(newEl, el.firstChild);
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$(selector).load(url, completeCallback)
// Native
fetch(url).then(data => data.text()).then(data => {
document.querySelector(selector).innerHTML = data
}).then(completeCallback)
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$(document).ready(eventHandler);
// Native
// Check if the DOMContentLoaded has already been completed
if (document.readyState === 'complete' || document.readyState !== 'loading') {
eventHandler();
} else {
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', eventHandler);
}
//jQuery
$el.clone();
//Native
el.cloneNode();
//jQuery
$el.empty();
//Native
el.innerHTML = '';
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$('.inner').unwrap();
// Native
Array.prototype.forEach.call(document.querySelectorAll('.inner'), (el) => {
Array.prototype.forEach.call(el.childNodes, (child) => {
el.parentNode.insertBefore(child, el);
});
el.parentNode.removeChild(el);
});
//jQuery
$('.inner').replaceWith('<div class="outer"></div>');
//Native
Array.prototype.forEach.call(document.querySelectorAll('.inner'),(el) => {
const outer = document.createElement("div");
outer.className = "outer";
el.parentNode.insertBefore(outer, el);
el.parentNode.removeChild(el);
});
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$el.on(eventName, eventHandler);
// Native
el.addEventListener(eventName, eventHandler);
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$(el).trigger('custom-event', {key1: 'data'});
// Native
if (window.CustomEvent) {
const event = new CustomEvent('custom-event', {detail: {key1: 'data'}});
} else {
const event = document.createEvent('CustomEvent');
event.initCustomEvent('custom-event', true, true, {key1: 'data'});
}
el.dispatchEvent(event);
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$.isArray(range);
// Native
Array.isArray(range);
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$.inArray(item, array);
// Native
array.indexOf(item) > -1;
// ES6-way
array.includes(item);
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$.extend({}, defaultOpts, opts);
// Native
Object.assign({}, defaultOpts, opts);
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$.each(array, (index, value) => {
});
// Native
array.forEach((value, index) => {
});
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$promise.done(doneCallback).fail(failCallback).always(alwaysCallback)
// Native
promise.then(doneCallback, failCallback).then(alwaysCallback, alwaysCallback)
// 这个 hack 也是醉了... 不一样吧. 第二个 then 可能返回了东西的
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
$.when($promise1, $promise2).done((promise1Result, promise2Result) => {
});
// Native
Promise.all([$promise1, $promise2]).then([promise1Result, promise2Result] => {});
// Deferred 是创建 promises 的一种方式。
// jQuery -------------------------------------------
function asyncFunc() {
const defer = new $.Deferred();
setTimeout(() => {
if(true) {
defer.resolve('some_value_computed_asynchronously');
} else {
defer.reject('failed');
}
}, 1000);
return defer.promise();
}
// Native
function asyncFunc() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (true) {
resolve('some_value_computed_asynchronously');
} else {
reject('failed');
}
}, 1000);
});
}
// Deferred way
function defer() {
const deferred = {};
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
deferred.resolve = resolve;
deferred.reject = reject;
});
deferred.promise = () => {
return promise;
};
return deferred;
}
function asyncFunc() {
const defer = defer();
setTimeout(() => {
if(true) {
defer.resolve('some_value_computed_asynchronously');
} else {
defer.reject('failed');
}
}, 1000);
return defer.promise();
}
4.7 INPROGRESS https://guide.freecodecamp.org/
4.7.1 DONE JavaScript
- 'let' has block scope, 'const' is const
- default parameters
- break, continue, continue with label 我不觉得这是很好的特性, pass
- Array.prototype
- concat, filter, forEach, find, includes,
- indexOf, lastIndexOf, map, pop, push, reduce, reduceRight,
- reverse, shift (shift to the left)
- every
- if callback return false, then stop and return false
- not mutating the array
- callback(element, index, array)
- some,
- sort,
- slice: Array.prototype.slice()
var animals = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant']; console.log(animals.slice(2)); // expected output: Array ["camel", "duck", "elephant"] console.log(animals.slice(2, 4)); // expected output: Array ["camel", "duck"] console.log(animals.slice(1, 5)); // expected output: Array ["bison", "camel", "duck", "elephant"]
- splice: Array.prototype.splice()
// syntax: // array.splice(start[, deleteCount[, item1[, item2[, ...]]]]) var myFish = ['angel', 'clown', 'mandarin', 'sturgeon']; myFish.splice(2, 0, 'drum'); // insert 'drum' at 2-index position // myFish is ["angel", "clown", "drum", "mandarin", "sturgeon"] myFish.splice(2, 1); // remove 1 item at 2-index position (that is, "drum") // myFish is ["angel", "clown", "mandarin", "sturgeon"] var myFish = ['angel', 'clown', 'mandarin', 'sturgeon']; var removed = myFish.splice(-2, 1); // myFish is ["angel", "clown", "sturgeon"] // removed is ["mandarin"] var myFish = ['angel', 'clown', 'mandarin', 'sturgeon']; var removed = myFish.splice(2); // myFish is ["angel", "clown"] // removed is ["mandarin", "sturgeon"]
- map, 顾名思义就可以用
- clear,
- forEach,
- size,
- get,
- set,
- delete,
- has,
- entries,
- keys,
- values,
- object
- keys
- hasOwnProperty
- promise TODO
- RegExp TODO
- string
- fromCharCode
- prototpy
- concot
- indexOf
- replace
- repeat
- slice
4.8 TODO Awesome Micro NPM Packages
4.8.1 TODO Articles
- One-line node modules
- Build small single purpose modules
- Module best practices
- Evaluating Packages Part 1 - Turn to community
- Evaluating Packages Part 2 - Review repository
- Small modules: it’s not quite that simple
- Hyper Modular Packages: A Crazy Cult or a Reasonable Practice?
- In Defense of Hyper Modular JavaScript
- Tiny npm package: Guidelines to create a Node.js module following the small package philosophy
- The cost of small modules
- Why I think "micro-packages" are a good thing.
4.8.2 Modules
- DONE Array
- is-sorted - A small module to check if an Array is sorted.
function defaultComparator (a, b) { return a - b } module.exports = function checksort (array, comparator) { comparator = comparator || defaultComparator for (var i = 1, length = array.length; i < length; ++i) { if (comparator(array[i - 1], array[i]) > 0) return false } return true } - :sad: array-first - Get the first element or first n elements of an array.
- array-last - Return the last element in an array. Faster than `slice`
var isNumber = require('is-number'); module.exports = function last(arr, n) { if (!Array.isArray(arr)) { throw new Error('expected the first argument to be an array'); } var len = arr.length; if (len === 0) { return null; } n = isNumber(n) ? +n : 1; if (n === 1) { return arr[len - 1]; } var res = new Array(n); while (n--) { res[n] = arr[--len]; } return res; }; - arr-flatten - Recursively flatten an array or arrays.
作者说是最快的 array flatten, 但… 真的看不到快的理由.
'use strict'; module.exports = function (arr) { return flat(arr, []); }; function flat(arr, res) { var i = 0, cur; var len = arr.length; for (; i < len; i++) { cur = arr[i]; Array.isArray(cur) ? flat(cur, res) : res.push(cur); } return res; } - dedupe - Remove duplicates from an array.
- array-range - Creates a new array with given range.
- arr-diff - Returns an array with only the unique values from the first array, by excluding all values from additional arrays using strict equality for comparisons.
- filled-array - Returns an array filled with the specified input
- map-array - Map object keys and values into an array.
- in-array - Return true if any of passed values exists in array - faster than using indexOf.
- unordered-array-remove - Efficiently remove an element from an unordered array without doing a splice.
- array-swap - Swap position of two items in an array.
- mirrarray - Creates a keymirror object from an array of valid keys.
- group-array - Group array of objects into lists.
- is-sorted - A small module to check if an Array is sorted.
4.10 SQL
4.10.1 sql 101
Although SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard, there are different versions of the SQL language.
SQL keywords are NOT case sensitive: select is the same as SELECT
Although SQL is an ANSI (American National Standards Institute) standard, there are different versions of the SQL language.
SQL keywords are NOT case sensitive: select is the same as SELECT
https://www.w3schools.com/sql/sql_quickref.asp
Some of The Most Important SQL Commands
- SELECT - extracts data from a database
- UPDATE - updates data in a database
- DELETE - deletes data from a database
- INSERT INTO - inserts new data into a database
- CREATE DATABASE - creates a new database
- ALTER DATABASE - modifies a database
- CREATE TABLE - creates a new table
- ALTER TABLE - modifies a table
- DROP TABLE - deletes a table
- CREATE INDEX - creates an index (search key)
- DROP INDEX - deletes an index
4.10.2 sql select, distinct, where, and/or/not, order by, insert into, null, update, delete
-- select
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name;
--
SELECT * FROM table_name;
-- distinct
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name;
-- where
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
-- and, or, not
WHERE condition1 AND condition2 AND condition3 ...;
WHERE NOT condition;
WHERE NOT Country='Germany' AND NOT Country='USA';
WHERE Country='Germany' AND (City='Berlin' OR City='München');
-- order by (default to asc)
ORDER BY column1, column2, ... ASC|DESC;
-- insert into
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...);
--
INSERT INTO Customers (CustomerName, ContactName, Address, City, PostalCode, Country)
VALUES ('Cardinal', 'Tom B. Erichsen', 'Skagen 21', 'Stavanger', '4006', 'Norway');
-- null
WHERE column_name IS NULL;
WHERE column_name IS NOT NULL;
-- update
UPDATE table_name
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2, ...
WHERE condition;
-- delete
DELETE FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
4.10.3 sql limits, min/max, count/avg/sum, like, between, alias
-- select top (count/percent), limits SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE condition LIMIT number; -- min, max SELECT MIN(column_name) FROM table_name WHERE condition; -- SELECT MIN(Price) AS SmallestPrice -- count, avg, sum COUNT(column_name) -- like SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE columnN LIKE pattern; -- WHERE CustomerName LIKE 'a%'; WHERE CustomerName LIKE '_r%'; WHERE City LIKE '[bsp]%'; WHERE City LIKE '[!bsp]%'; WHERE City NOT LIKE '[bsp]%'; -- column in operator SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE column_name IN (value1, value2, ...); -- SELECT * FROM Customers WHERE Country NOT IN (SELECT Country FROM Suppliers); -- between WHERE column_name BETWEEN value1 AND value2; -- WHERE Price BETWEEN 10 AND 20; WHERE Price NOT BETWEEN 10 AND 20; WHERE OrderDate BETWEEN #27/04/1996# AND #27/09/1996#; -- alias column SELECT column_name AS alias_name FROM table_name; -- alias table SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name AS alias_name; -- SELECT CustomerName AS Customer, ContactName AS [Contact Person] FROM Customers; -- SELECT CustomerName, CONCAT(Address,',',PostalCode,',',City,',',Country) AS Address FROM Customers;
4.10.4 sql join (inner, outer (left,right,full))
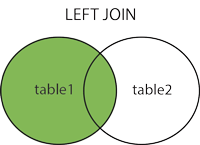
Here are the different types of the JOINs in SQL:
- (INNER) JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables
- LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table
- RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table
- FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Return all records when there is a match in either left or right table
-- inner join SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name; -- SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Shippers.ShipperName FROM ((Orders INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID) INNER JOIN Shippers ON Orders.ShipperID = Shippers.ShipperID); -- left join SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 LEFT JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name; -- right join SELECT Orders.OrderID, Employees.LastName, Employees.FirstName FROM Orders RIGHT JOIN Employees ON Orders.EmployeeID = Employees.EmployeeID ORDER BY Orders.OrderID; -- full outer join SELECT column_name(s) FROM table1 FULL OUTER JOIN table2 ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name; -- SQL Self JOIN A self JOIN is a regular join, but the table is joined with itself. SELECT A.CustomerName AS CustomerName1, B.CustomerName AS CustomerName2, A.City FROM Customers A, Customers B WHERE A.CustomerID <> B.CustomerID AND A.City = B.City ORDER BY A.City;
4.10.5 sql union, group by, having, exsists, any/all
SELECT City FROM Customers UNION SELECT City FROM Suppliers ORDER BY City; -- no dups SELECT City FROM Customers UNION ALL SELECT City FROM Suppliers ORDER BY City; -- SELECT City, Country FROM Customers WHERE Country='Germany' UNION SELECT City, Country FROM Suppliers WHERE Country='Germany' ORDER BY City; -- group by The GROUP BY statement is often used with aggregate functions (COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM, AVG) to group the result-set by one or more columns. SELECT COUNT(CustomerID), Country FROM Customers GROUP BY Country; -- having The HAVING clause was added to SQL because the WHERE keyword could not be used with aggregate functions. -- SELECT COUNT(CustomerID), Country FROM Customers GROUP BY Country HAVING COUNT(CustomerID) > 5; -- SELECT Employees.LastName, COUNT(Orders.OrderID) AS NumberOfOrders FROM (Orders INNER JOIN Employees ON Orders.EmployeeID = Employees.EmployeeID) GROUP BY LastName HAVING COUNT(Orders.OrderID) > 10; -- exists SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE EXISTS (SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE condition); -- any, all The following SQL statement returns TRUE and lists the productnames if it finds ANY records in the OrderDetails table that quantity = 10: -- SELECT ProductName FROM Products WHERE ProductID = ANY (SELECT ProductID FROM OrderDetails WHERE Quantity = 10); -- The following SQL statement returns TRUE and lists the productnames if ALL the records in the OrderDetails table has quantity = 10: SELECT ProductName FROM Products WHERE ProductID = ALL (SELECT ProductID FROM OrderDetails WHERE Quantity = 10);
4.10.6 sql select into, insert into, null
-- select into (直接新建 table)
The SELECT INTO statement copies data from one table into a new table.
SELECT * INTO CustomersBackup2017
FROM Customers;
-- create table from another one
SELECT * INTO newtable
FROM oldtable
WHERE 1 = 0;
-- insert into
INSERT INTO table2
SELECT * FROM table1
WHERE condition;
--
INSERT INTO Customers (CustomerName, City, Country)
SELECT SupplierName, City, Country FROM Suppliers;
-- null functions: ifnull
SELECT ProductName, UnitPrice * (UnitsInStock + IFNULL(UnitsOnOrder, 0))
FROM Products
--
SELECT ProductName, UnitPrice * (UnitsInStock + COALESCE(UnitsOnOrder, 0))
FROM Products
CREATE DATABASE databasename;
DROP DATABASE databasename;
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype,
column2 datatype,
column3 datatype,
....
);
CREATE TABLE new_table_name AS
SELECT column1, column2,...
FROM existing_table_name
WHERE ....;
DROP TABLE table_name;
-- delete entries but not the table itself
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;
ALTER TABLE table_name
--> ADD column_name datatype;
--> DROP COLUMN column_name;
--> ALTER COLUMN column_name datatype;
--> MODIFY COLUMN column_name datatype;
4.10.7 sql constraints
The following constraints are commonly used in SQL:
- NOT NULL - Ensures that a column cannot have a NULL value
- UNIQUE - Ensures that all values in a column are different
- PRIMARY KEY - A combination of a NOT NULL and UNIQUE. Uniquely identifies each row in a table
- FOREIGN KEY - Uniquely identifies a row/record in another table
- CHECK - Ensures that all values in a column satisfies a specific condition
- DEFAULT - Sets a default value for a column when no value is specified
- INDEX - Used to create and retrieve data from the database very quickly
-- constraints
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column1 datatype constraint,
column2 datatype constraint,
column3 datatype constraint,
....
);
-- primary key
CREATE TABLE Persons (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
CREATE TABLE Persons (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
CONSTRAINT PK_Person PRIMARY KEY (ID,LastName)
);
-- foreign key
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID int NOT NULL,
OrderNumber int NOT NULL,
PersonID int,
PRIMARY KEY (OrderID),
FOREIGN KEY (PersonID) REFERENCES Persons(PersonID)
);
ALTER TABLE Orders
ADD FOREIGN KEY (PersonID) REFERENCES Persons(PersonID);
--
ALTER TABLE Orders
ADD CONSTRAINT FK_PersonOrder FOREIGN KEY (PersonID) REFERENCES Persons(PersonID);
--
ALTER TABLE Orders
DROP FOREIGN KEY FK_PersonOrder;
--
ALTER TABLE Orders
DROP CONSTRAINT FK_PersonOrder;
CREATE TABLE Persons (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
CHECK (Age>=18)
);
--
CREATE TABLE Persons (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
City varchar(255),
CONSTRAINT CHK_Person CHECK (Age>=18 AND City='Sandnes')
);
--
ALTER TABLE Persons
ADD CHECK (Age>=18);
--
ALTER TABLE Persons
ADD CONSTRAINT CHK_PersonAge CHECK (Age>=18 AND City='Sandnes');
-- defaults
CREATE TABLE Persons (
ID int NOT NULL,
LastName varchar(255) NOT NULL,
FirstName varchar(255),
Age int,
OrderDate date DEFAULT GETDATE(),
City varchar(255) DEFAULT 'Sandnes'
);
--
ALTER TABLE Persons
ALTER City SET DEFAULT 'Sandnes';
--
ALTER TABLE Persons
ALTER City DROP DEFAULT;
CREATE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (column1, column2, ...);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name
ON table_name (column1, column2, ...);
ALTER TABLE table_name
DROP INDEX index_name;
-- auto increment
ID int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
ALTER TABLE Persons AUTO_INCREMENT=100;
INSERT INTO Persons (FirstName,LastName)
VALUES ('Lars','Monsen');
-- view
CREATE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
--
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_name AS
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
DROP VIEW view_name;